1.Punjab Haldi 1:
2.Punjab Haldi 2:
Popular Variety : Amalapuram, Armour, Dindigam, Erode, Krishna, Kodur, Vontimitra, P317, GL Purm I and II, RH2 and RH10
Rajapuri, Salem, Sangli turmeric, Nizamabad bulb.
Soil –
Climate –
Time of sowing
Seed Rate
Seed treatment
Spacing
Method of sowing
Direct sowing and transplanting method is used for planting.
Fertilizer Requirement (kg/acre)
| UREA | SSP | MURIATE OF POTASH |
| 25 | 60 | 16 |
Nutrient Requirement (kg/acre)
| NITROGEN | PHOSPHORUS | POTASH |
| 10 | 10 | 10 |
1) Rhizome fly:
2)Sucking pest:

To control sucking pests take spray of neem based pesticide like Azadirachtin 0.3EC@ 2 ml/Ltr of water.
3)Shoot borer:

If infestation of shoot borer is observed, take spray of Dimethoate@250ml/150Ltr or Quinalphos@250ml/150Ltr of water to control shoot borer.
1.Nitrogen
|
| Deficiency Symptoms |
|
| Correction Measure |
Application of 140 kg N/ha in the form of Urea in five split doses viz. at planting, 30, 60, 90 and 120 DAP along with 60 kg P2O5 and 60 Kg K2O or foliar spray of DAP 2% or 1% Urea twice at weekly interval. |
2.Phosphorus
|
| Deficiency Symptoms |
|
| Correction Measure |
|
4.Potassium
|
| Deficiency Symptoms |
Reduced growth, shortened internodes, marginal burn or scorch (brown leaf edges), necrotic (dead) spots in the leaf, reduction of lateral breaks and tendency to wilt readily. |
| Correction Measure |
Application of K at 90 kg/ha in four splits (basal, 60, 90 and 120 DAP) or foliar spray of K2SO4 at 1% at fortnightly interval |
5.Sulpher
|
| Deficiency Symptoms |
Stunted plant growth, leaves turn to pale yellow, finally chlorosis symptoms will occur. |
| Correction Measure |
Foliar spray of Magnesium sulphate solution (5g MgSo4 dissolved in 1 lit of water) +10g urea in the interval of 15 days on the foliage till the symptoms disappear |
6.Manganese
|
| Deficiency Symptoms |
|
| Correction Measure |
Spray with Manganese Sulphate solution 0.5% twice at meekly intervals. |
7.Iron
|
| Deficiency Symptoms |
|
| Correction Measure |
Soil application of FeSO4 at 30kg/ha followed by foliar spray of FeSO4 (2.5 kg/ha) during 3rd, 4th and 5th months |
1) Blight and leaf spots:
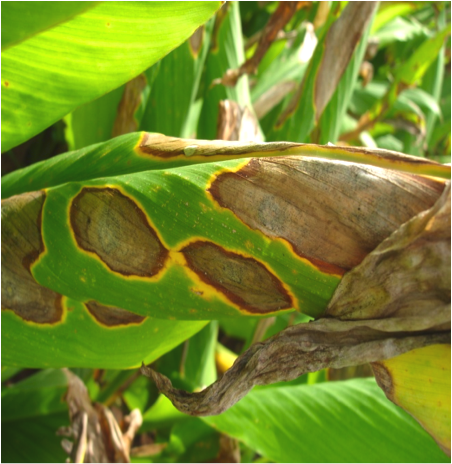

Symptoms-
Management-
2) Root or Rhizome Rot :

Symptoms
Management-
To prevent crop from root rot, drench crop with Mancozeb@3gm / Ltr at 30, 60 and 90 days after planting.
3) Bacterial wilt :

Management-
To prevent crop from bacterial wilt, drench plants with Copper oxychloride @3 gm / Ltr of water immediately after disease is seen in field.

Symptoms
Management-
Fresh rhizomes: 25-30 t/ha,
Cured rhizomes: 5-6 t/ha
Growing Districts Karur, Villupuram, Coimbatore, Salem, Dharmapuri, Krishnagiri, Erode
Major markets in Tamil Nadu Erode, Karur, Coimbatore, Salem and Dharmapuri
Grade designation Alleppey Finger Turmeric, Rajapure Finger Turmeric
Grade specification Bright Yellow colour, size above 3cm length, hard, when broken gives metal sound , smooth skin , without impurities
